Table of Contents
- Chickenpox 1 - “Chickenpox” Every year, there is a growing population ...
- Infographic - Chickenpox - CHICKENPOX people who never had chickenpox ...
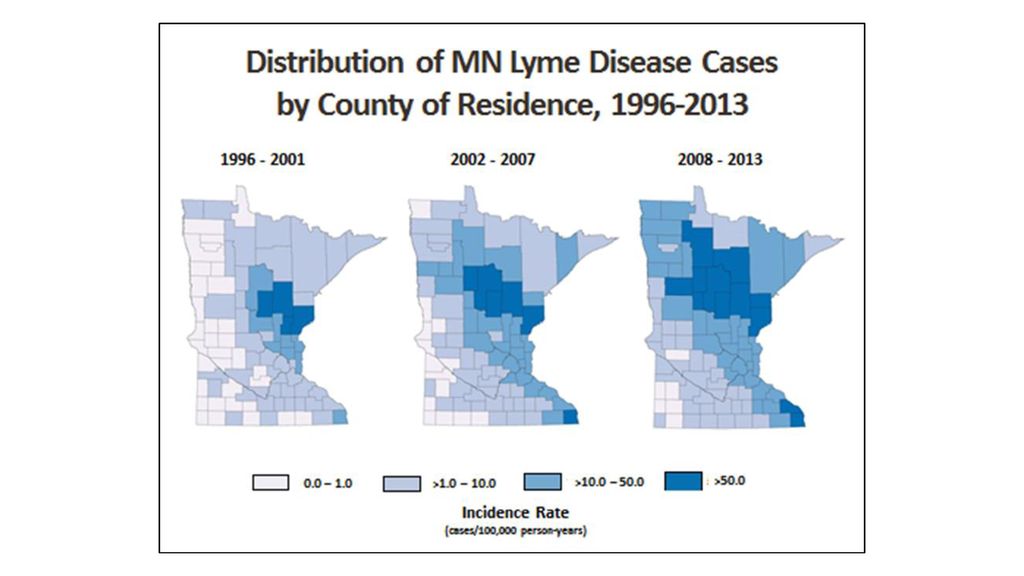
- Ticks & Tickborne Diseases of Minnesota - ppt download
- Incidences of chickenpox Germany | Statista
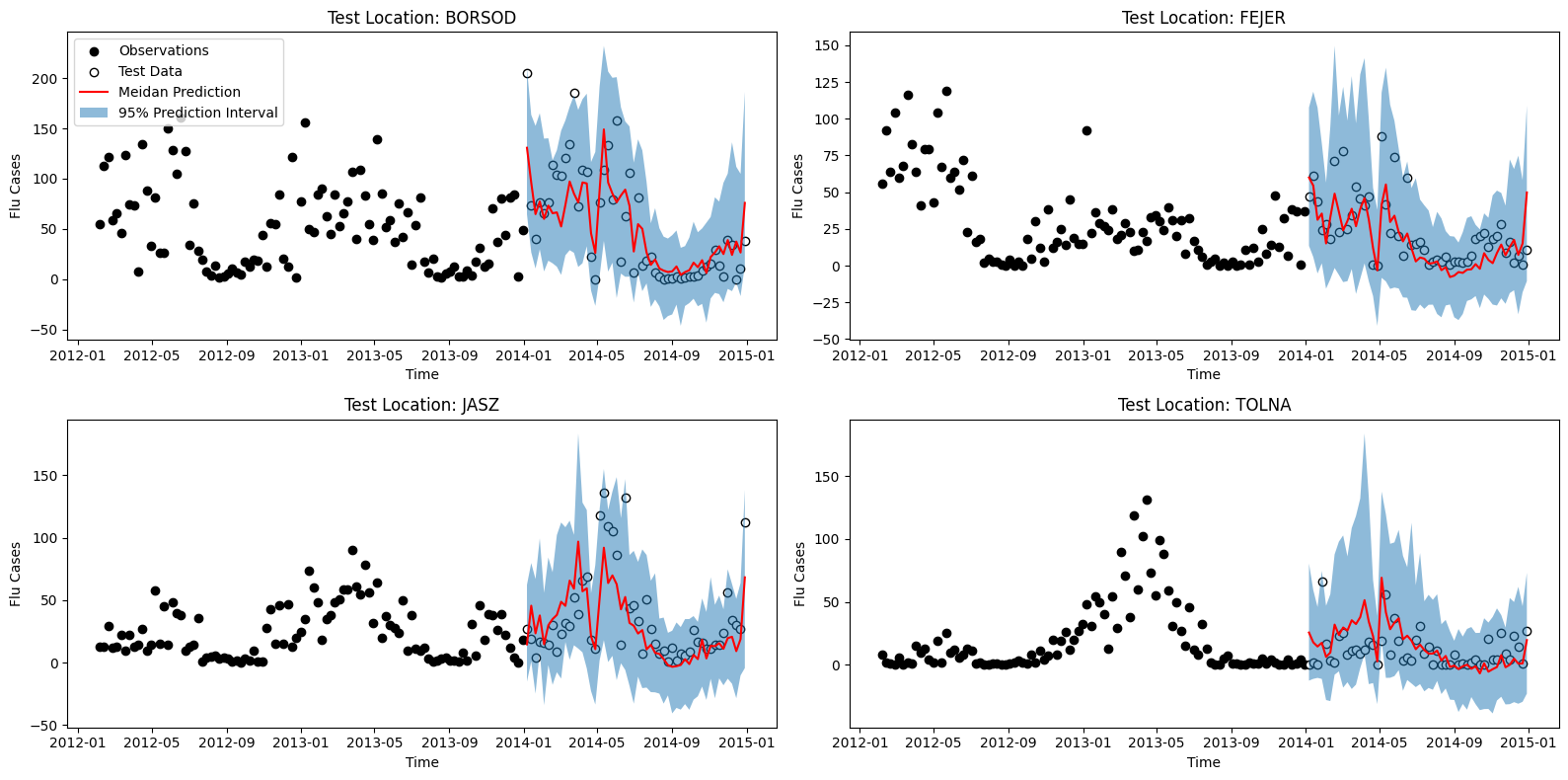
- Hungarian Chickenpox - bayesnf
- Chicken Pox Virus
- [PDF] Rising Trends of Chicken Pox Outbreaks among School Children in ...
- New variant of chickenpox in India; know the symptoms and prevention tips
- showed that Median Endemic Index of chickenpox cases in Najaf in May ...
- Declining incidence of chickenpox in the absence of universal childhood ...


Varicella (Chickenpox) Statistics
![[PDF] Rising Trends of Chicken Pox Outbreaks among School Children in ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/85a0968ff20e975c87721cc20361cc75779bd759/5-Figure5-1.png)
- The majority of varicella cases occur among children under the age of 10.
- The peak season for varicella is typically during the winter and early spring months.
- Unvaccinated individuals are at a higher risk of contracting varicella and experiencing complications.


Zoster (Shingles) Statistics


- Most zoster cases occur among adults over the age of 50.
- The risk of developing zoster increases with age, with the highest rates seen among those over 80.
- Certain medical conditions, such as weakened immune systems, can increase the risk of developing zoster.
Public Health Implications
The Varicella and Zoster Annual Statistics Summaries provided by the MN Dept. of Health have important implications for public health. The data suggest that:- Vaccination remains a critical tool in preventing varicella and zoster infections.
- Targeted interventions, such as vaccination campaigns and outreach programs, can help reduce the risk of outbreaks and complications.
- Healthcare providers should be aware of the risks and symptoms of varicella and zoster, particularly among vulnerable populations such as older adults and young children.
For more information on varicella and zoster, including prevention and treatment options, visit the MN Dept. of Health website. Stay informed, stay healthy!
Note: The article is written in HTML format with header tags (h1, h2), unordered lists (ul), and a link to the MN Dept. of Health website. The content is optimized for search engines with relevant keywords, such as "Varicella and Zoster Annual Statistics Summaries", "MN Dept. of Health", and "public health".